
1 R2, R
Divergence of a radial 1 / r 2 vector field Ask Question Asked 9 years, 3 months ago Modified 6 years, 1 month ago Viewed 5k times 2 How to obtain the divergence of the function F(r, φ, θ) = ˆr / r2 where ˆr is the unit vector in radial direction? Is there a solution without computing the surface integral for definition of divergence?

Pin on Math Videos
Here are some basic characteristics of the measure: Since r 2 is a proportion, it is always a number between 0 and 1.; If r 2 = 1, all of the data points fall perfectly on the regression line. The predictor x accounts for all of the variation in y!; If r 2 = 0, the estimated regression line is perfectly horizontal. The predictor x accounts for none of the variation in y!

R(2) YouTube
The " coefficient of determination " or " R-squared value ," denoted R 2, is the regression sum of squares divided by the total sum of squares. Alternatively (as demonstrated in the video below), since SSTO = SSR + SSE, the quantity R 2 also equals one minus the ratio of the error sum of squares to the total sum of squares:

In the given circuit , `R_1 != R_2` and the reading of the voltmeter is the same, irrespective
(y1-y_bar)^2 + (y2-y_bar)^2 + (y3-y_bar)^2 = (1-2)^2 + (2-2)^2 + (3-2)^2 = 2. this is going to be a very small fraction over here. 1 minus a very small fraction is going to be a number close to 1. So then, our R-squared will be close to 1, which tells us that a lot of the variation in y is described by the variation in x. Which makes sense.
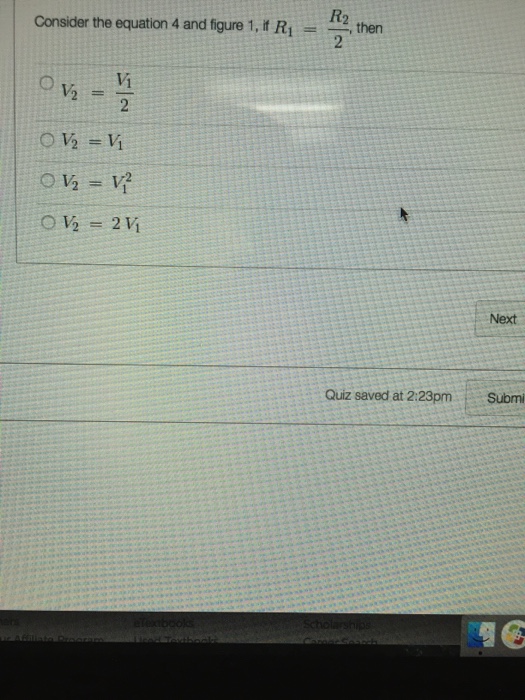
Solved Consider the equation 4 and figure 1, if R_1 = R_2/2,
Popular Problems Algebra Factor r^2+2r+1 r2 + 2r + 1 r 2 + 2 r + 1 Rewrite 1 1 as 12 1 2. r2 + 2r+12 r 2 + 2 r + 1 2 Check that the middle term is two times the product of the numbers being squared in the first term and third term. 2r = 2⋅r ⋅1 2 r = 2 ⋅ r ⋅ 1 Rewrite the polynomial. r2 + 2⋅r⋅1+12 r 2 + 2 ⋅ r ⋅ 1 + 1 2

Two resistance r1 and r2(r1
The distance square in the Newton's law of universal gravitation is really a square? (7 answers) Closed 9 years ago. Is there something intrinsic about the structure of space that gravity is proportional to 1/r^2 instead of, for example, 1/r^2.143 ? What makes the exponent turn out to be a nice even number? newtonian-gravity Share Cite
Line graph of the number of coupled r 1 , r 2 values for which the... Download Scientific Diagram
High School Math Solutions - Radical Equation Calculator. Radical equations are equations involving radicals of any order. We will show examples of square roots; higher. Read More. Save to Notebook! Sign in. Free solve for a variable calculator - solve the equation for different variables step-by-step.

Question What is does the (R) in this photo mean? chemistry
About Transcript A finite geometric series can be solved using the formula a (1-rⁿ)/ (1-r). Sal demonstrates how to derive a formula for the sum of the first 'n' terms of such a series, emphasizing the importance of understanding the number of terms being summed. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted averynash
ElWx_oe7gkHeBFbiV1qJuDqVeaeYMl777CWL5Bz0Pei4OHZAc_o8sqBYDsLQtR1s2I3axrvz=s900ckc0x00ffffffnorj
Calculus Evaluate the Integral integral of 1/ (r^2) with respect to r ∫ 1 r2 dr ∫ 1 r 2 d r Apply basic rules of exponents. Tap for more steps. ∫ r−2dr ∫ r - 2 d r By the Power Rule, the integral of r−2 r - 2 with respect to r r is −r−1 - r - 1. −r−1 +C - r - 1 + C Rewrite −r−1 +C - r - 1 + C as −1 r +C - 1 r + C. −1 r +C - 1 r + C

R...(2) YouTube
Published on April 22, 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on June 22, 2023. The coefficient of determination is a number between 0 and 1 that measures how well a statistical model predicts an outcome. The coefficient of determination is often written as R2, which is pronounced as "r squared."
vzaIEyJYmE1t3xmF_WSIx2EBSJq3myCUCKxEwO_mFWyuSoHjhon4dzIfrCCfuANSaibJ99PA=s900ckc0x00ffffff
Calculus Simplify (1-r^2)/ (1-r) 1 − r2 1 − r 1 - r 2 1 - r Simplify the numerator. Tap for more steps. (1+r)(1− r) 1−r ( 1 + r) ( 1 - r) 1 - r Cancel the common factor of 1−r 1 - r. Tap for more steps. 1+r 1 + r

A student carries out an experiment and plots the `VI` graphs of three samples of nichrome wire
You can find the gradient of $1/r$ more easily using the chain rule and the identity $\nabla r^2 = 2 \vec r$. In particular, $$\nabla \frac{1}{r} = \nabla \frac{1}{\sqrt{r^2}} =- \frac{1}{2 (r^2)^{3/2}} \nabla r^2 =-\frac{\vec r}{ r^3} = -\frac{\hat r}{r^2}$$ Finally, in evaluating the problem $\nabla \cdot \hat r$, you can use the product rule:
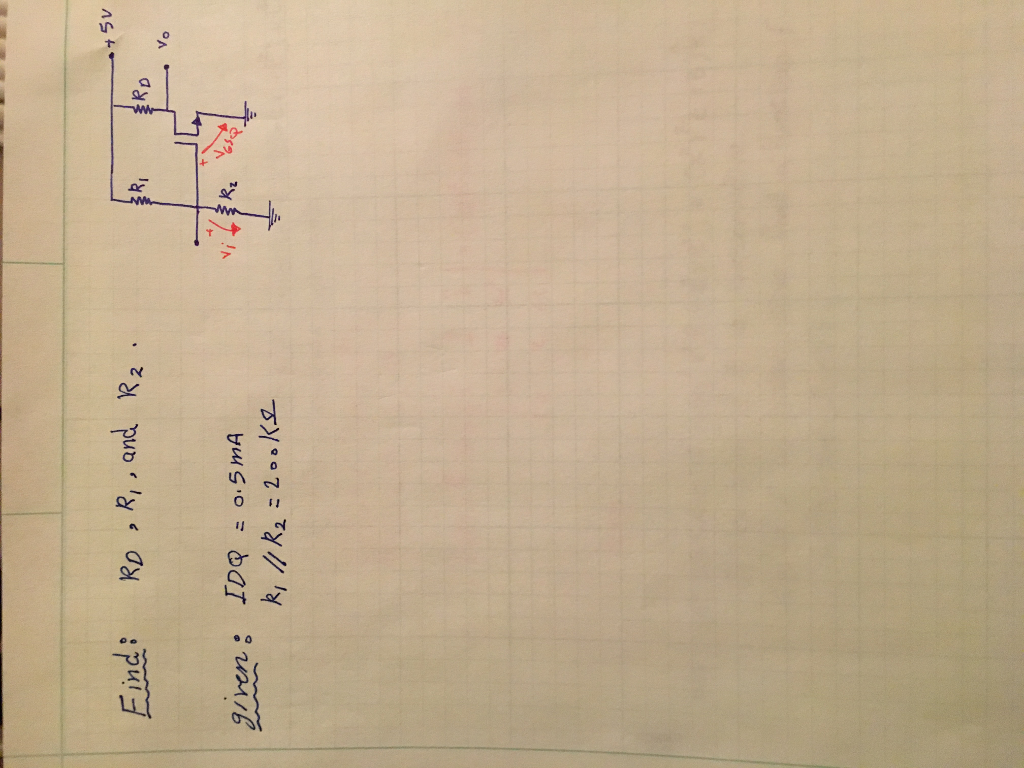
Solved Find R_D, R_1, and R_2 Given IDQ = 0.5 mA
In the real world, the inverse square law (squared distance law) I ~ 1/ r2 is always an idealization because it assumes exactly equal sound intensity or acoustic intensity I as sound energy propagation in all directions. If there are reflective surfaces in the sound field,

1_r_2
Components Coefficient a The first nine terms of geometric series 1 + r + r2 + r3. drawn as functions (colored in the order red, green, blue, red, green, blue,.) within the range | r | < 1. The closed form geometric series 1 / (1 - r) is the black dashed line. The geometric series a + ar + ar2 + ar3 +. is written in expanded form. [1]
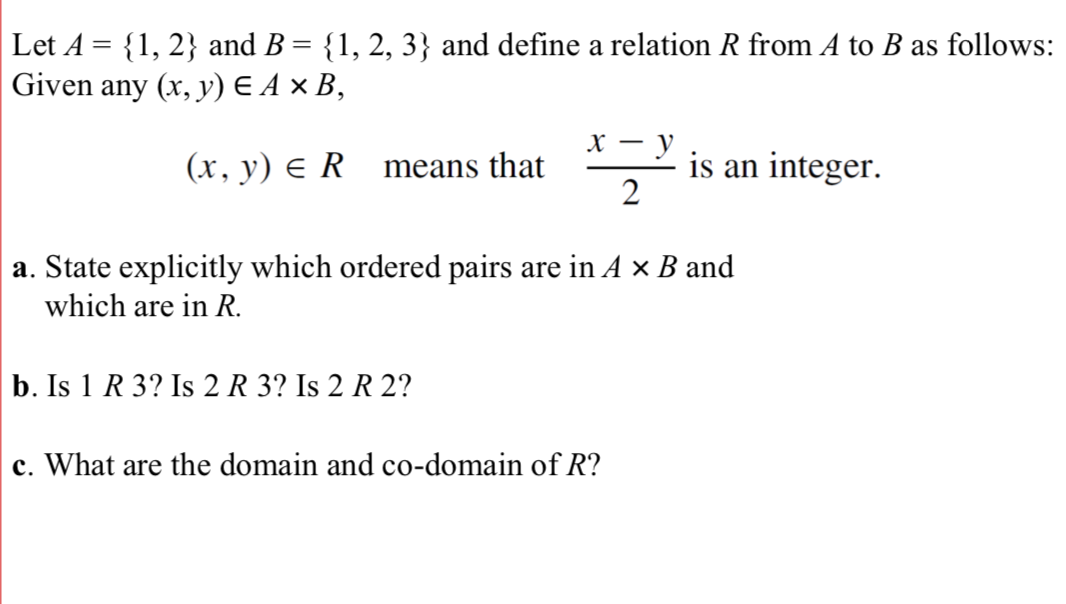
Answered Let A 1, 2} and B = {1, 2, 3} and… bartleby
Gravitation Gravitation is the attraction between objects that have mass. Newton's law states: The gravitational attraction force between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their separation distance.
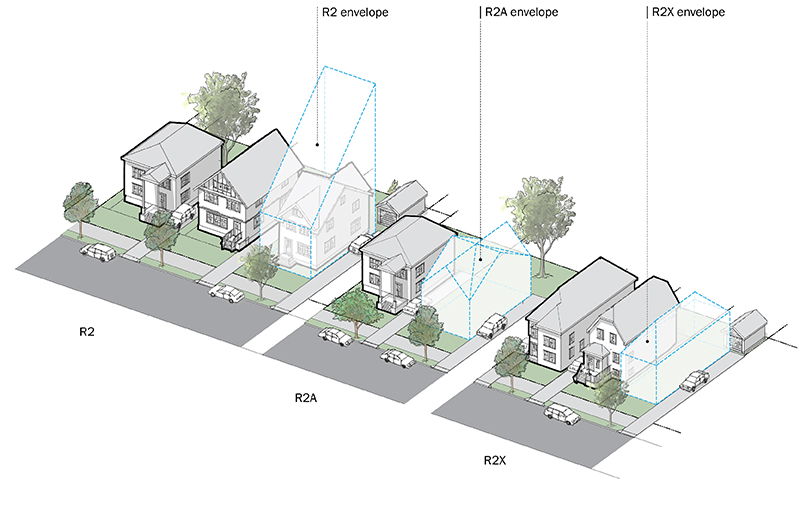
Zoning; know the difference between R1 and R2D2? Daily Index
Massless photon case: Now, the 1 / r potential gives rise to a force that goes as 1 / r 2. This force decreases as the area of the sphere of radius r, indicating that the force 1 / r 2 is a purely geometrical fact of 3 spatial dimensions: intuitively, we emit N photons from a point and the force decreases with the surface density of the photons.