
Boron An essential mineral that improves absorption of calcium and magnesium Health
A possible crystal structure of Boron is rhombohedral structure. In metals, and in many other solids, the atoms are arranged in regular arrays called crystals. A crystal lattice is a repeating pattern of mathematical points that extends throughout space. The forces of chemical bonding causes this repetition.

Boron Definition, Occurrence, Properties and Uses Embibe
Podcasts The Naked Scientists. Periodic Table of Videos Created by video journalist Brady Haran working with chemists at The University of Nottingham. Element Boron (B), Group 13, Atomic Number 5, p-block, Mass 10.81. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images.

How To Find The Electron Configuration For Boron Dynamic Periodic Table of Elements and Chemistry
In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Boron atom (B). We'll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons ar.

boron Properties, Uses, & Facts Britannica
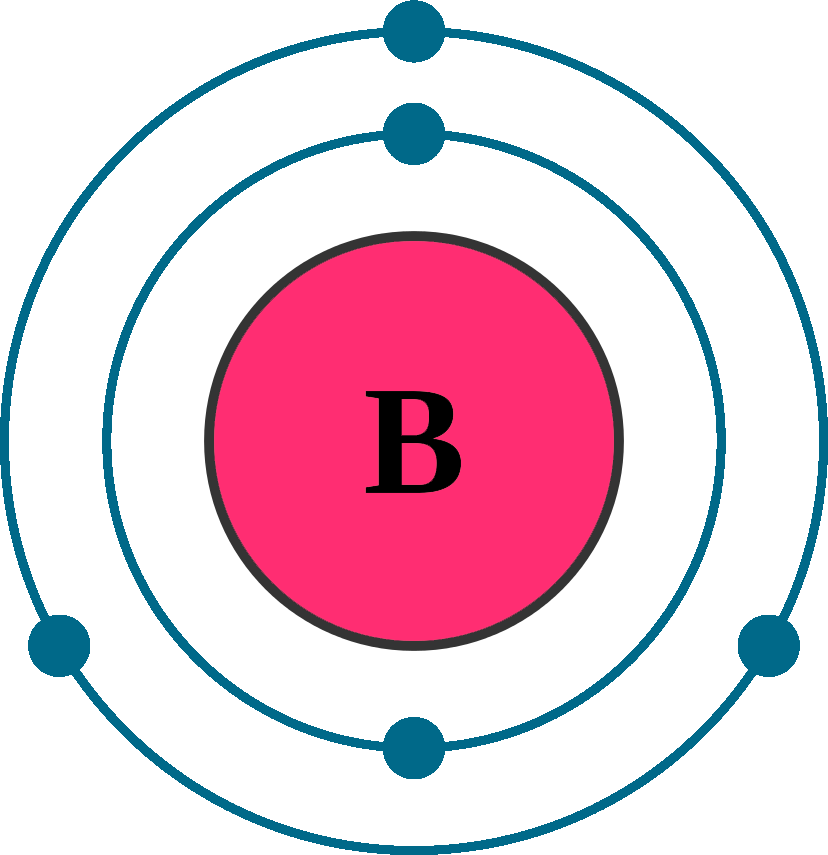
Boron is a chemical element with atomic number 5 which means there are 5 protons and 5 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Boron is B. Significant concentrations of boron occur on the Earth in compounds known as the borate minerals.
Boron Element With Reaction, Properties, Uses, & Price Periodic Table
Boron group element - Properties, Uses, Atomic Structure: The table gives a list of some properties of the boron group elements. The ionization energies suggest that the formation of salts of the M2+ ions might be feasible. At first glance, such appears to be the case, since gallium compounds with the formula GaX2 (X representing chlorine, bromine, or iodine) can be made, and similar cases.

Boron, atomic structure Stock Image C045/6392 Science Photo Library
Amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares to provide a distinctive green color, and in rockets as an igniter. By far the most commercially important boron compound in terms of dollar sales is Na 2 B 4 O 7 • 5H2O. Th i s pentahydrate is used in very large quantities in the manufacture of insulation fiberglass and sodium perborate bleach.. Boric acid is also an important boron compound.

Chemical Elements atomic_structure_of_boron_color Classroom Clipart
boron (B), chemical element, semimetal of main Group 13 (IIIa, or boron group) of the periodic table, essential to plant growth and of wide industrial application. Properties, occurrence, and uses

Atom Diagrams Boron Atom Atomic Structures Pinterest Search and Atoms
The mass of one atom is usually expressed in atomic mass units (amu), which is referred to as the atomic mass. An amu is defined as exactly 1/12 1 / 12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom and is equal to 1.6605 × × 10 −24 g. Protons are relatively heavy particles with a charge of 1+ and a mass of 1.0073 amu.

Boron, atomic structure Stock Image C018/3686 Science Photo Library
2.04. Atomic Radius. 90 pm. Stable Isotopes. 10 B, 11 B. Boron is the only element in group 3 that is not a metal. It has properties that lie between metals and non-metals (semimetals). For example Boron is a semiconductor unlike the rest of the group 13 elements. Chemically, it is closer to aluminum than any of the other group 13 elements.

Boron10 Isotope AMERICAN ELEMENTS
Figure 23.4.4 23.4. 4: The Structures of ScB 12 and CaB 6, Two Boron-Rich Metal Borides. (a) The structure of ScB12 consists of B12 clusters and Sc atoms arranged in a faced-centered cubic lattice similar to that of NaCl, with B12units occupying the anion positions and scandium atoms the cation positions.
Boron, Atomic Model Photograph by Friedrich Saurer Fine Art America
What is Boron. Boron (pronunciation BO-ron [2]), represented by the chemical symbol or chemical formula B [1], is hard and brittle in its crystalline form [22].It has allotropes in the form of an amorphous powder and three major crystalline forms [34].Naturally occurring B has two stable isotopes with mass numbers 10 and 11 [1, 2].Besides that, it has 11 synthetic isotopes, some of which are.
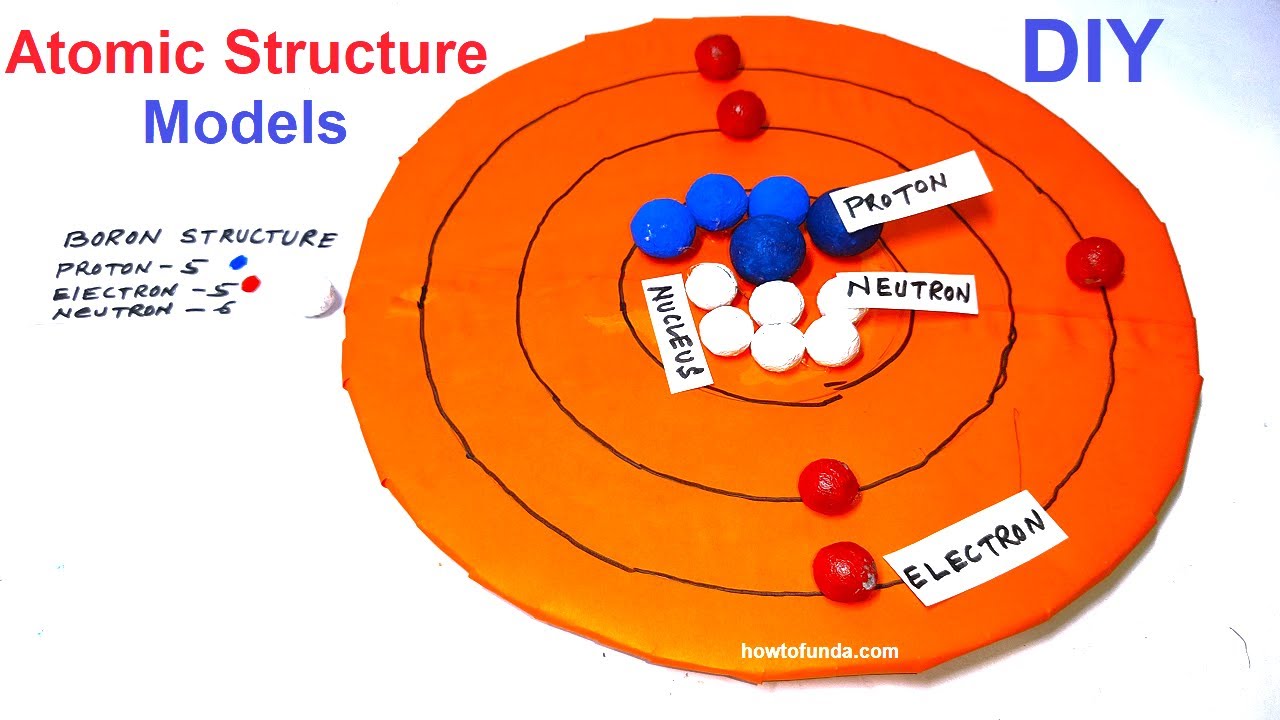
atomic structure models atom structure boron 3d atomic models diy howtofunda class 9
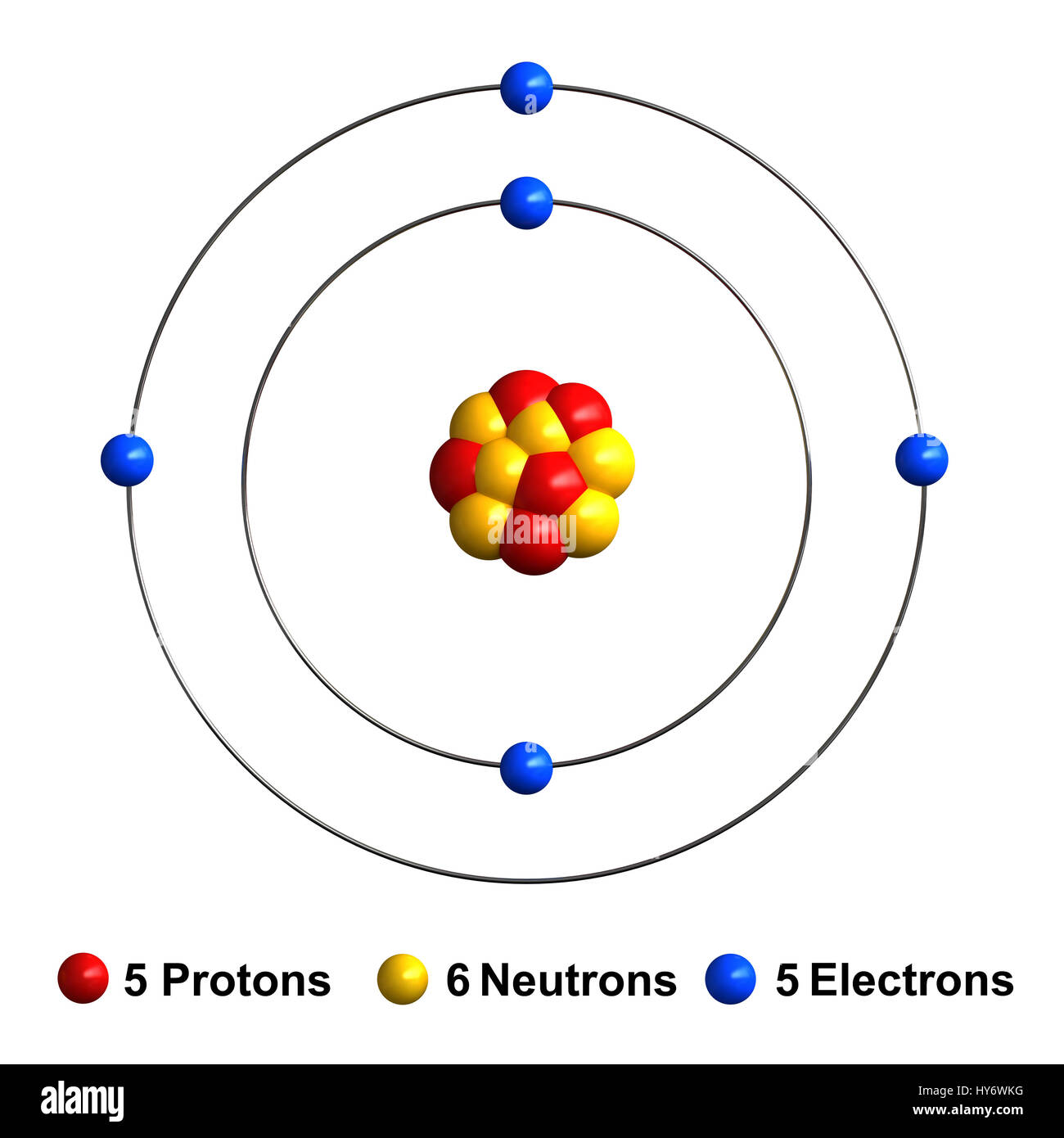
Name: Boron Symbol: B Atomic Number: 5 Atomic Mass: 10.811 amu Melting Point: 2300.0 °C (2573.15 K, 4172.0 °F) Boiling Point: 2550.0 °C (2823.15 K, 4622.0 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 5 Number of Neutrons: 6 Classification: Metalloid Crystal Structure: Rhombohedral Density @ 293 K: 2.34 g/cm 3 Color: brownish Atomic Structure
Estructura Atómica De Boro Fotos e Imágenes de stock Alamy
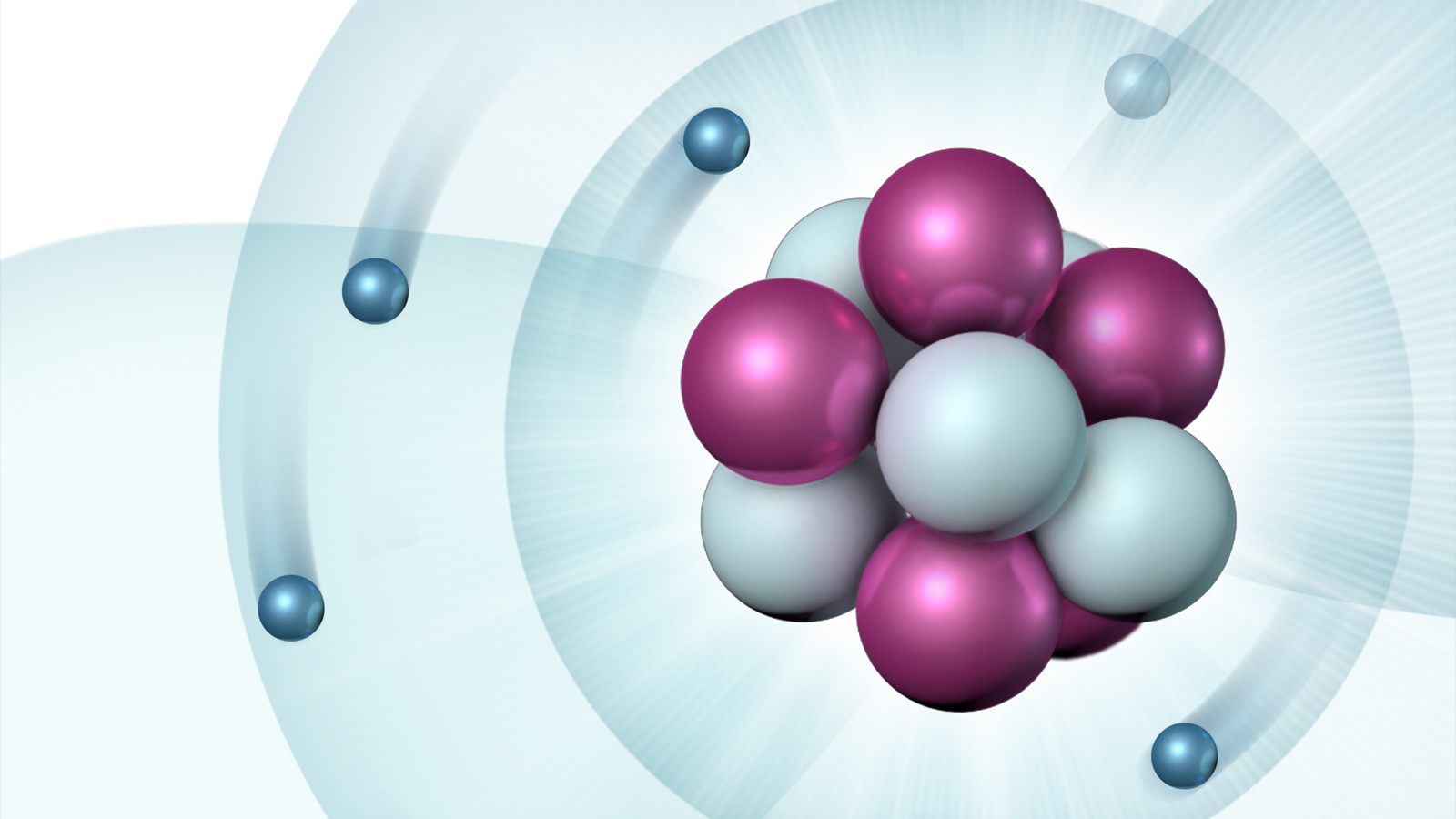
Atomic Structure of Boron The atomic number of the boron element is 5. The nucleus of this atom consists of six neutrons and five positively charged protons. Five electrons occupy available electron shells and revolve around the nucleus. The stability of the valence electrons determines the chemical and physical properties of the element.
😊 Boron element. 5. 20190124
To name a few, (i) unlike carbon with its typical bonding patterns (such as sp 2 and sp 3 ), the chemical bonding of boron is highly flexible and complex; 1 (ii) the most stable structures of boron clusters, B 80 as a famous example, are generally unknown; (iii) the ground state structure of boron crystals has not been conclusively determined in.
Combination of experiments and calculations allows examination of boron’s complicated dance
1. Introduction. The mysteries of boron have persisted in chemistry since the discovery of the B 2 H 6 molecule. To name a few, (i) unlike carbon with its typical bonding patterns (such as sp 2 and sp 3), the chemical bonding of boron is highly flexible and complex;1 (ii) the most stable structures of boron clusters, B 80 as a famous example, are generally unknown; (iii) the ground state.

Boron Photograph by Science Photo Library Fine Art America
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder.