The Plasma Membrane Structure Anatomy & Physiology
The plasma membrane is the easiest cell membrane to label because it is very accessible. Fluorescent dyes and most commonly used dyes FM 1-43 family are used for labeling the plasma membrane. The cytosol is the intracellular space excluding the nucleus and the organelles.

Plant Cell Membrane
11. protein type that spans the plasma membrane Activity 2: Label the Drawing. The illustration of the plasma membrane is from your lesson. Test your memory of the structural components and their.

Plasma Membrane Location, Structure Functions Class 9 CBSE Class
Over 90% Of All Products On eBay Are Brand New. Big Brands, Top Retailers. Great Prices On Millions Of Items. Get It On eBay.

Image and Video Gallery National Institute of General Medical Sciences
The plasma membrane is a protective barrier that surrounds the interior of the cell. Also called the cell membrane, this structure is semi-porous and allows certain molecules in and out of the cell. It serves as a boundary by keeping the cell's contents inside and preventing them from spilling out.
DNA TIPS Technical Difficulties The Cell Membrane
On the Web: cell membrane, thin membrane that surrounds every living cell, delimiting the cell from the environment around it. Enclosed by this cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) are the cell's constituents, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and substances.
The building blocks of cells
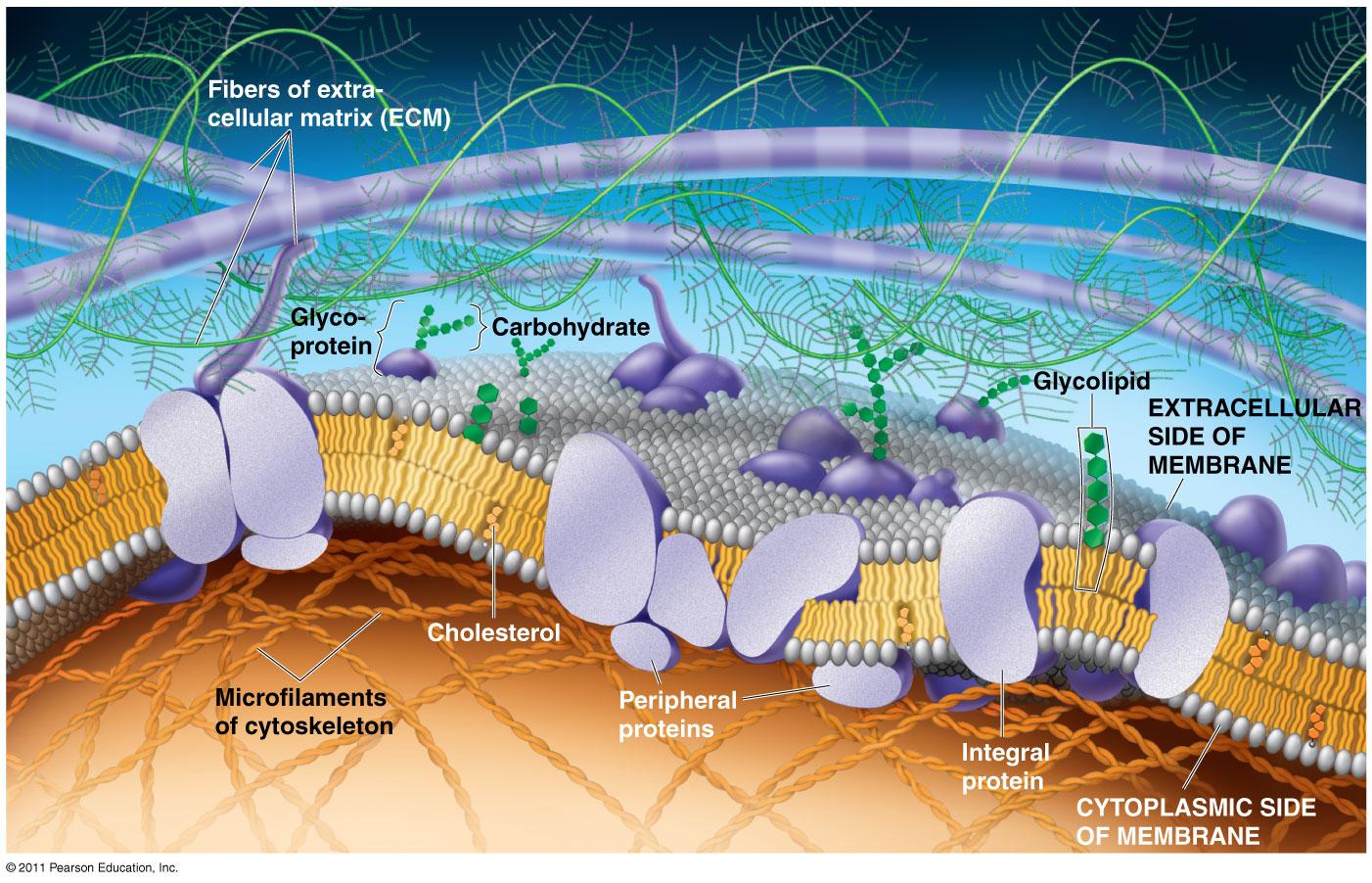
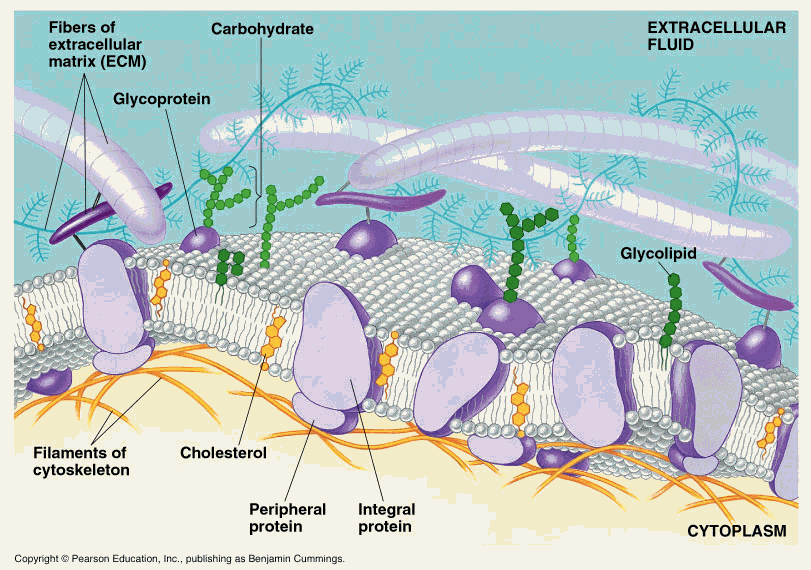
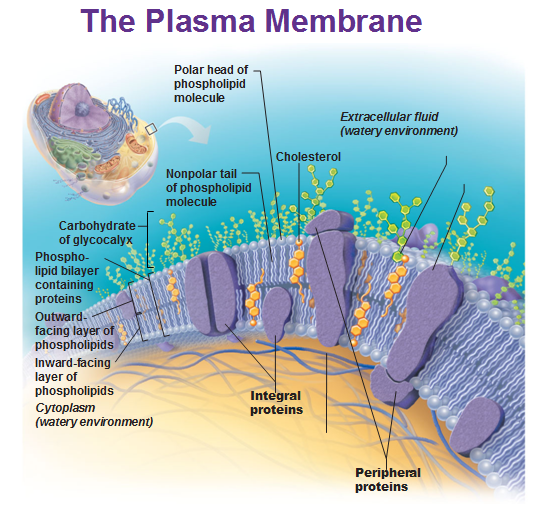
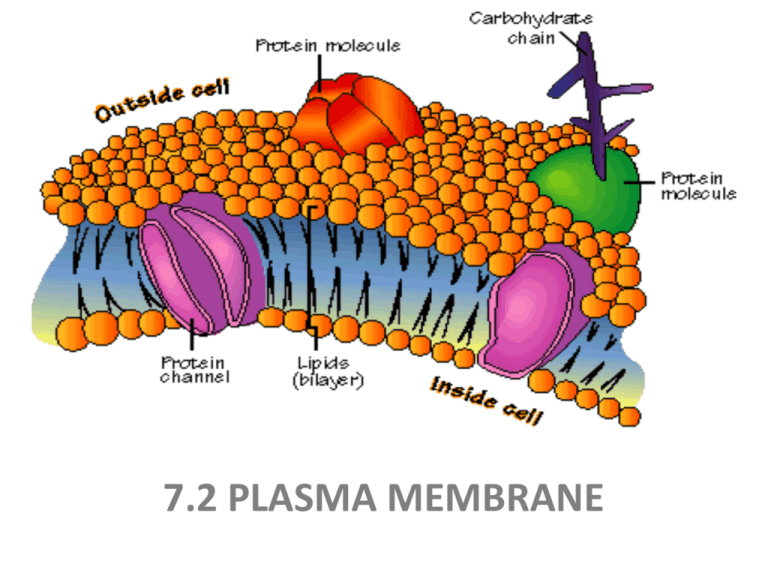
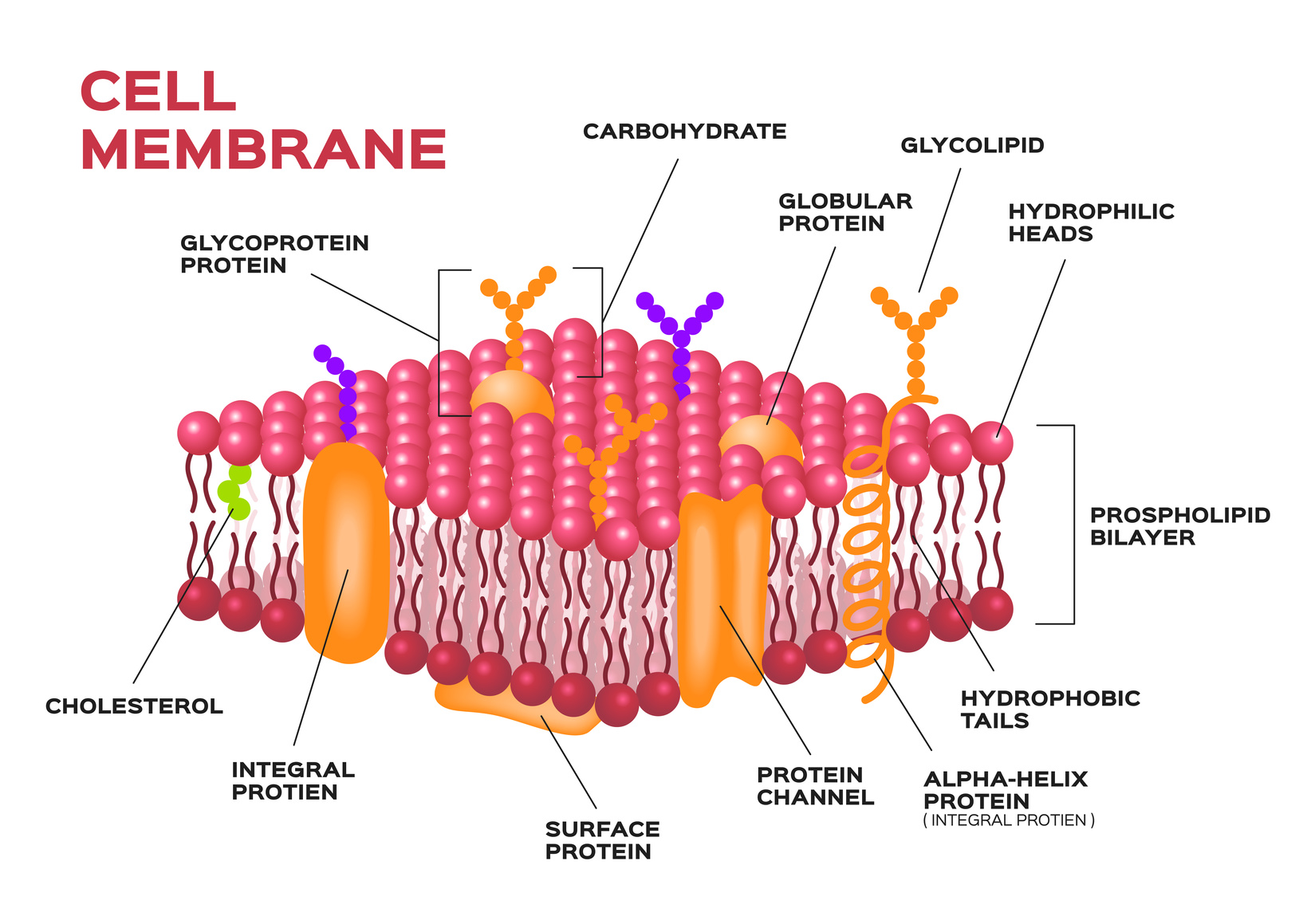
Key Points. The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids ( phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrates. The plasma membrane protects intracellular components from the extracellular environment. The plasma membrane mediates cellular processes by regulating the materials that enter and exit the cell.
STRUCTURE of PLASMA MEMBRANE
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, separates the interior of the cell from the extracellular environment. It is composed of about 50% lipids and 50% proteins.
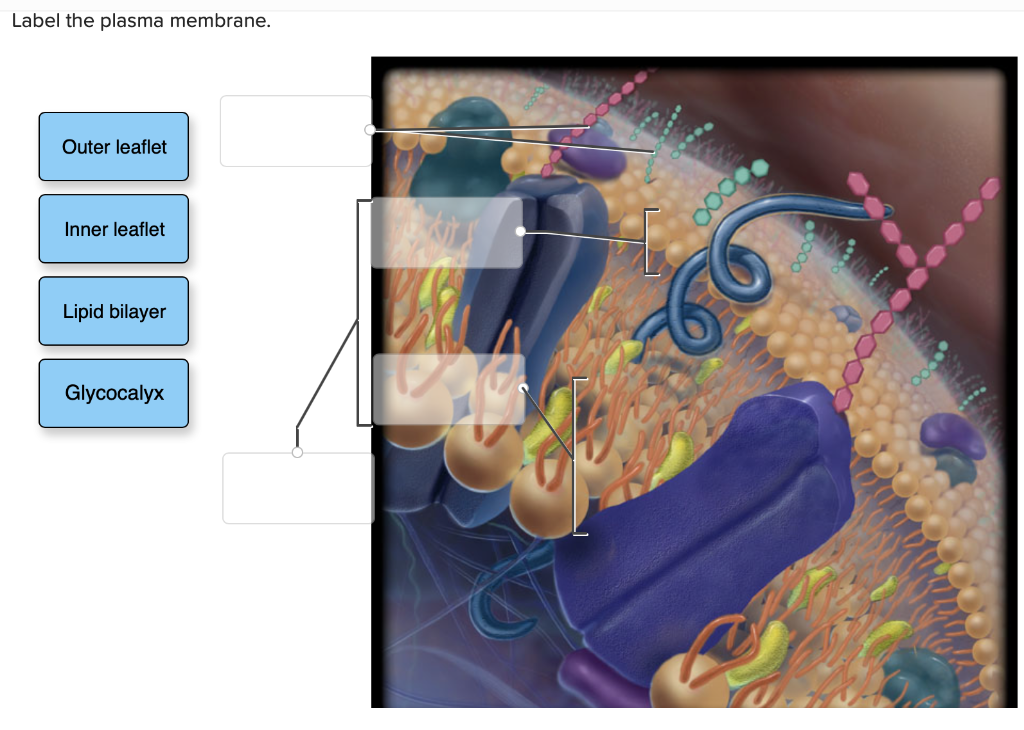
Solved Label the plasma membrane. Outer leaflet Inner
The plasma membrane is the border between the interior and exterior of a cell. As such, it controls passage of various molecules—including sugars, amino acids, ions, and water—into and out of the cell. How easily these molecules can cross the membrane depends on their size and polarity.

Khan Academy Plasma membrane, Biology diagrams, Math printables
Figure 2.4.1 2.4. 1: Animal cell model. The plasma membrane is a structure that forms a barrier between the cytoplasm inside the cell and the environment outside the cell. Without the plasma membrane, there would be no cell. The membrane also protects and supports the cell and controls everything that enters and leaves it.

ANTPHY 1 Study Guide (201415 Lykins) Instructor Lykins at University
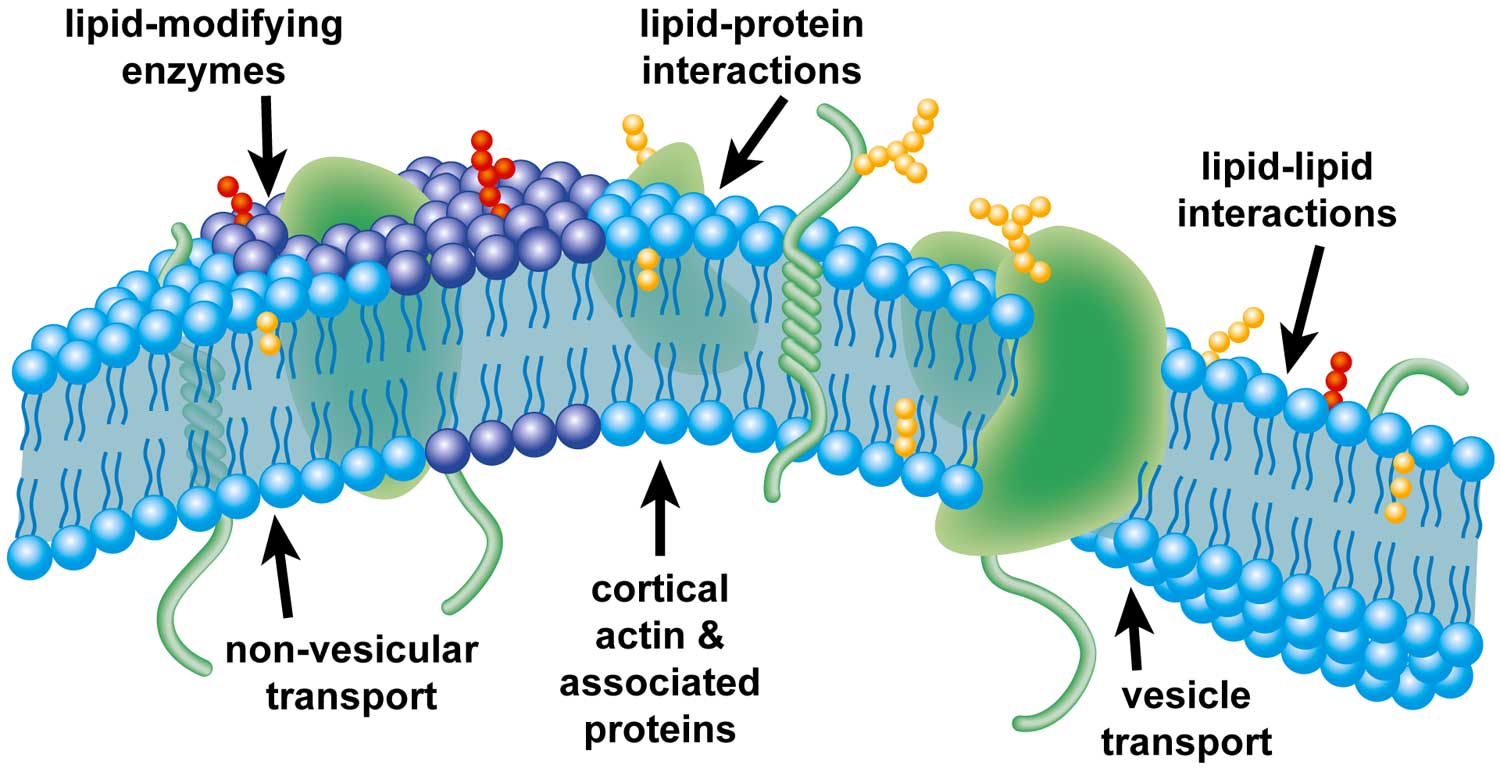
Membrane Proteins Can Be Associated with the Lipid Bilayer in Various Ways. Different membrane proteins are associated with the membranes in different ways, as illustrated in Figure 10-17.Many extend through the lipid bilayer, with part of their mass on either side (examples 1, 2, and 3 in Figure 10-17).Like their lipid neighbors, these transmembrane proteins are amphipathic, having regions.

Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane, Pharmacology nursing, Endocrine
The plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cell's contents and the outside of the cell. It is also simply called the cell membrane. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment.
Phosphatidylserine Review Top Memory Pill May Boost Mental Performance
The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png)
Cell Membrane Function and Structure
Structure and Composition of the Cell Membrane The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two layers of phospholipids (a "bilayer"). Cholesterol and various proteins are also embedded within the membrane giving the membrane a variety of functions described below.

Cell Membrane Labeled Cell Membrane Structure, Plasma Membrane, Biology
Secondary active transport moves multiple molecules across the membrane, powering the uphill movement of one molecule(s) (A) with the downhill movement of the other(s) (B). For example, SGLT2 is a glucose transporter that allows glucose (Molecule A) into our cells (against its gradient) by bringing in a sodium molecule (Molecule B) as well.
Membrane Structure and Diffusion Biology Quizizz
According to the fluid mosaic model, the plasma membrane is a mosaic of components—primarily, phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins—that move freely and fluidly in the plane of the membrane.

Who discovered fluid mosaic model of plasma membra
Design Labels Like a Pro with Our Customizable Label Templates! Download or Create Label Templates for Online Office Software